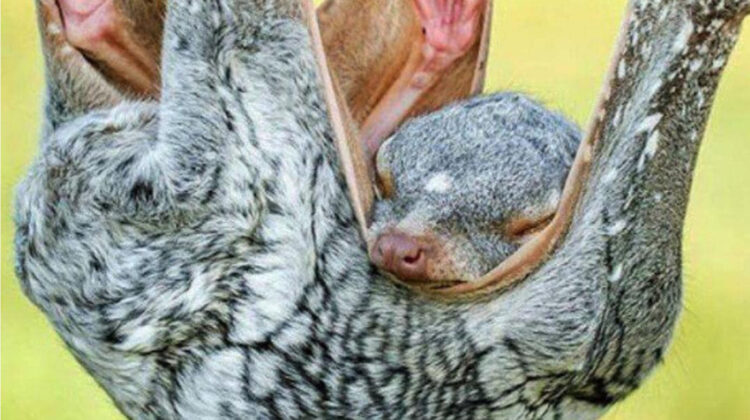

Colugos are arboreal gliding mammals that are native to Southeast Asia. Their closest evolutionary relatives are primates. There are just two living species of colugos: the Sunda flying lemur (Galeopterus variegatus) and the Philippine flying lemur (Cynocephalus volans). These two species make up the entire family Cynocephalidae and order Dermoptera (not to be confused with Dermaptera, an order of insects known as earwigs).
Although they are called “flying lemurs“, the colugos are not lemurs and do not fly. Instead, they glide as they leap among trees. They are the most capable gliders of all gliding mammals. A fur-covered membrane, called a patagium, connects to the face, paws, and tail. This enables them to glide in the air for distances of up to 200 metres (660 ft) between trees. They are also known as cobegos.
Characteristics
Appearance and anatomy
They reach lengths of 35 to 40 cm (14 to 16 in) and weigh 1 to 2 kg (2.2 to 4.4 lb). They have long, slender front and rear limbs, a medium-length tail, and a relatively light build. The head is small, with large, front-focused eyes for excellent binocular vision, and small rounded ears.
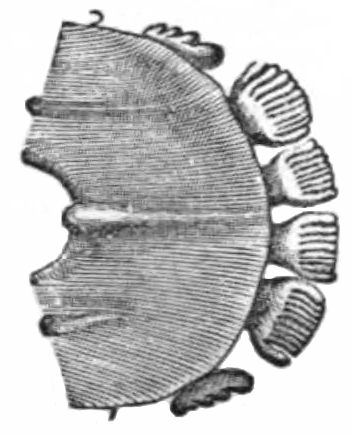
The incisor teeth of colugos are highly distinctive; they are comb-like in shape with up to 20 tines on each tooth. The incisors are analogous in appearance and function to the incisor suite in strepsirrhines, which is used for grooming. The second upper incisors have two roots, another unique feature among mammals. The dental formula of colugos is: 2.1.2.33.1.2.3
Movement
Colugos are proficient gliders, and they can travel as far as 70 m (230 ft) from one tree to another without losing much altitude, with a Malayan colugo (Galeopterus variegatus) individual having travelled about 150 m (490 ft) in one glide.
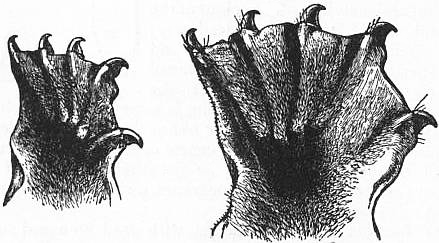
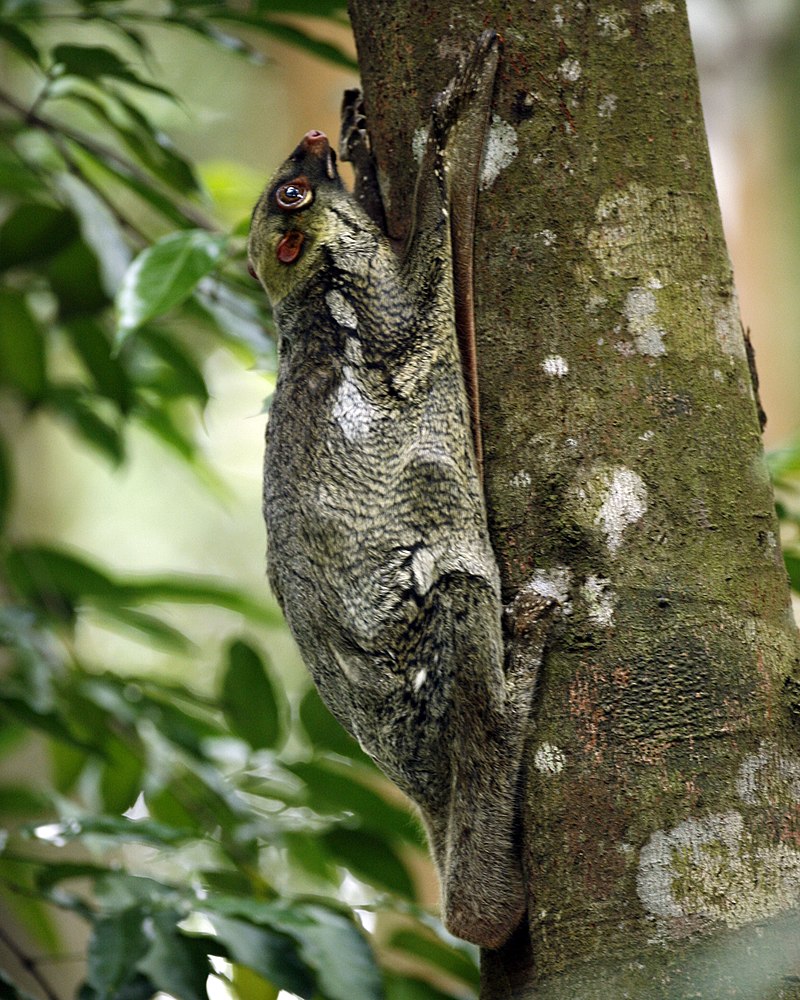
Of all the gliding mammals, colugos have the most perfected adaptation for flight. They have a large membrane of skin that extends between their paired limbs and gives them the ability to glide significant distances between trees. This gliding membrane, or patagium, runs from the shoulder blades to the fore paws, from the tip of the rear-most fingers to the tip of the toes, and from the hind legs to the tip of the tail. The spaces between the colugo’s fingers and toes are webbed. As a result, colugos were once considered to be close relatives of bats. Today, on account of genetic data, they are considered to be more closely related to primates.
Lower jaw (Galeopterus).
Colugos are unskilled climbers; they lack opposable thumbs. They progress up trees in a series of slow hops, gripping onto the bark with their small, sharp claws. They spend most of the day resting. At night, colugos spend most of their time up in the trees foraging, with gliding being used to either find another foraging tree or to find possible mates and protect territory.
Behavior and diet
Colugos are shy, nocturnal, solitary animals found in the tropical forests of Southeast Asia. Consequently, very little is known about their behavior. They are herbivorous and eat leaves, shoots, flowers, sap, and fruit. They have well-developed stomachs and long intestines capable of extracting nutrients from leaves and other fibrous material.
Colugos have evolved into a nocturnal species, along with the ability to proficiently see during the nighttime.
Lifecycle
Although they are placental mammals, colugos raise their young in a manner similar to marsupials. Newborn colugos are underdeveloped and weigh only 35 g (1.2 oz). They spend the first six months of life clinging to their mother’s belly. The mother colugo curls her tail and folds her patagium into a warm, secure, quasipouch to protect and transport her young. The young do not reach maturity until they are two to three years old. In captivity, they live up to 15 years, but their lifespan in the wild is unknown.
Status
Both species are threatened by habitat destruction, and the Philippine flying lemur was once classified by the IUCN as vulnerable. In 1996, the IUCN declared the species vulnerable owing to destruction of lowland forests and hunting. It was downlisted to least-concern status in 2008 but still faces the same threats. In addition to the ongoing clearing of its rainforest habitat, it is hunted for its meat and fur. It is also a favorite prey item for the gravely endangered Philippine eagle; some studies suggest colugos account for 90% of the eagle’s diet.



Leave a Reply